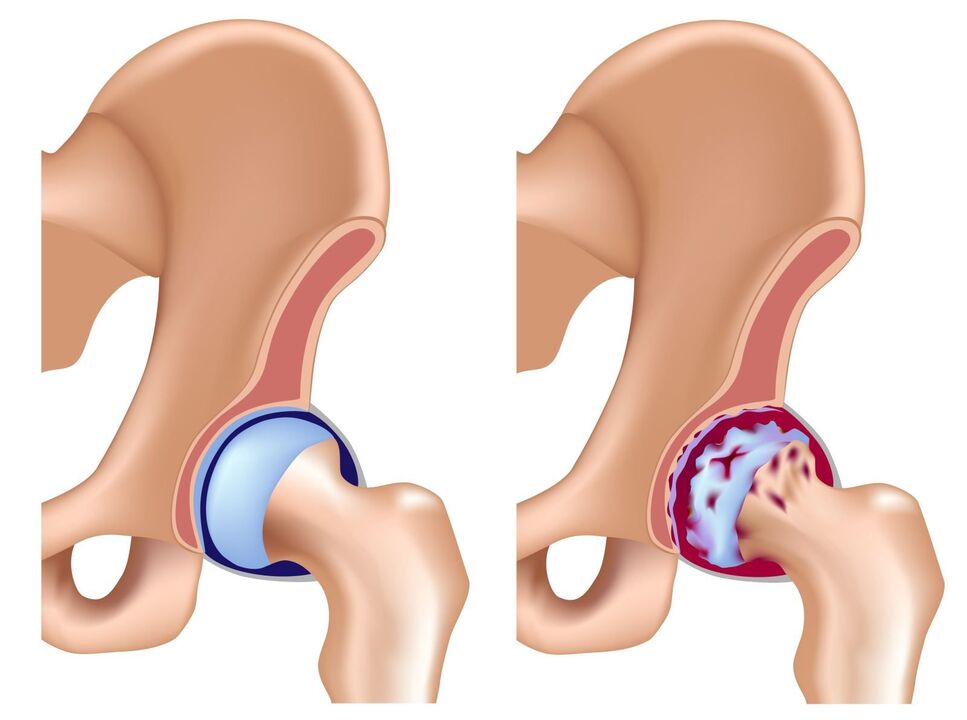
Coxarthrosis is a disease of the hip joints caused by changes in the structure of the tissues in them.The disease has another name - arthrosis of the hip joint or osteoarthritis.
Coxarthrosis is a complex degenerative disease caused by changes in the cartilage tissue of the joint.Cartilage tissue cannot be restored after the formation of the human skeleton is completed, so any damage to it affects the condition of the tissue in the future.The condition of the cartilage is also affected by the joint fluid, which performs the function of lubricating the tissues.Due to insufficient lubrication and increased friction, the articular cartilage thins and eventually wears out completely.The lack of cartilage leads to an increase in the load on the surface of the bones, friction occurs between the bones, which leads to a change in their shape and position, which leads to the appearance of pain.
Most often, elderly people suffer from coxarthrosis, because at that time the functions of cartilage tissue are lost.
Types of coxarthrosis
In medicine, primary and secondary coxarthrosis are distinguished.
In the primary case, the causes of the disease are unclear.
The development of secondary coxarthrosis is influenced by the following reasons:
- receiving various injuries and fractures;
- birth defects in the hip joint (congenital luxation of the hip joint);
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the hip area;
- rheumatoid arthritis (a connective tissue disease that destroys joint cartilage);
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head (death of the femoral head).
Stages of coxarthrosis
In medical practice, there are 4 stages of coxarthrosis:
Stage 1
It is characterized by the appearance of periodic pain in the joint.The pain occurs when you begin to move after a state of rest, but disappears in the process of resuming vigorous activity.In a calm state, pain does not appear.Joint mobility is not impaired.X-ray shows small bony growths and slight narrowing of the joint space.
Stage 2
The appearance of pain during moderate physical activity, as well as at rest.The appearance of lameness during prolonged walking.Knee or lower back pain may occur.X-ray shows: changes in the shape of the head of the femur, uneven bone contour, thickening of the bone neck, significant growth of bone tissue, narrowing of the joint space 2 times.
Stage 3
Constant pain occurs regardless of physical activity, both in an active and at rest state.Pain can cause insomnia.Due to the limited mobility of the joint, a person is forced to walk with support.Radiography revealed a significant increase in the width of the neck of the bone and a decrease in its length compared to the norm and deformation of the head of the femur.The joint space is practically absent.Physical condition is severely limited.The patient may be recognized as disabled.
Stage 4
The patient experiences excruciating pain at rest.Any movement causes severe pain, the patient cannot move with support (crutches, cane).The only method of treating coxarthrosis is surgical.
Causes of coxarthrosis
The appearance of coxarthrosis is influenced by many reasons, but the most important is impaired blood circulation in the hip area.Due to improper blood circulation, the metabolism in the joints slows down and this leads to gradual atrophy of the leg muscles.
Other causes of coxarthrosis are:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- microtraumas that do not cause pain to the patient;
- endocrine disorders;
- changes in the joint surfaces due to age;
- increased load on the joints (most often in athletes);
- inflammatory and infectious processes in the joints;
- pathologies of the foot (flat feet) and spine (scoliosis);
- obesity (increased load on the joint due to excess weight) and other reasons.
Taking into account the health status of the whole organism, the exact causes of the disease in a particular patient are determined.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
Cosarthrosis affects men and women after 40 years.Women experience more painful symptoms.
Signs of coxarthrosis are:
- pain in the hip joint (occurs periodically and is painful in nature);
- uneven, unsteady gait (limping);
- the appearance of crunch in the joint;
- the mobility of the injured leg is limited (at the initial stage, one feels heaviness and stiffness in movements, fatigue and general malaise);
- the appearance of atrophy of the muscles of the thigh (the volume and tone of the muscles change, causing pain in the knee).
Diagnosis of coxarthrosis
To determine the diagnosis of coxarthrosis, it is necessary to undergo diagnostic procedures:
- examination of the patient by a specialist;
- Carrying out general and biochemical blood tests (allows us to identify inflammatory processes and distinguish arthritis from arthrosis);
- X-rays (used to detect damage and changes in bone tissue);
- nuclear magnetic resonance of the joint (reveals minor changes in cartilage tissue).
Treatment of coxarthrosis
To treat the disease, specialists use medical procedures and drugs.
Treatment methods for coxarthrosis include:
- therapeutic exercises and massage;
- physical therapy;
- ozone therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- drug treatment;
- surgical treatment, etc.
In specialized clinics, an individual program for the treatment of coxarthrosis is selected for each patient, taking into account his age, concomitant diseases and stage of coxarthrosis.The individual approach contributes to the fastest possible recovery of the patient.
Therapeutic gymnastics and massage
Gymnastics helps strengthen muscles and improve blood circulation.Morning exercises not only wake up the body after sleep, but also raise the synovial fluid from the lower parts of the joint.Synovial fluid lubricates the cartilage tissue with essential nutrients that increase the cartilage's resistance to stress throughout the day.
But with coxarthrosis, physical exercises should be chosen wisely.Too sharp and vigorous movements can cause severe pain and injure the joint.It is recommended to go to the pool, as swimming helps strengthen muscles, relieves tension on the joint and does not cause injuries.
Massage for coxarthrosis is a very effective and safe method.Improves blood circulation, strengthens muscles, relieves painful spasms, swelling and muscle tension.During a massage of the hip joint, lower back and back, the muscles relax, due to which the synovial fluid is distributed throughout the cartilage.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy combines different methods:
- electrotherapy;
- UHF therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- laser therapy;
- paraffin therapy, etc.
All these procedures are aimed at improving blood circulation, relieving spasms and inflammation, this is due to the fact that access to the hip joint is limited.
Drug treatment
There are many drugs that perform different functions in the treatment of coxarthrosis:
- Topical drugs(ointments, compresses, lotions).Under the influence of advertising, most patients believe that treatment with various ointments and creams is the most effective way.However, this is a misconception, as the healing properties of such drugs are unable to reach the hip joint due to its deep location.They only help to temporarily improve blood circulation and relieve spasms.The causes of coxarthrosis have not been eliminated and the disease continues to gradually develop into a more complicated stage.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.They are used to eliminate inflammatory processes, relieve swelling and pain.As a result of long-term use of non-steroidal drugs, side effects occur that negatively affect the internal organs (gastritis).These drugs do not restore the cartilage tissue needed for normal joint function.
- Muscle relaxants(medicines that relax muscles).They improve blood circulation and relieve muscle tension around the joint.The effect of the drugs is temporary, joint functions are not restored.
- Hormonal steroid drugs.Intra-articular hormonal injections help with concomitant diseases, for example, with inflammation of the tendons of the femur.They have side effects and a short-term therapeutic effect.
- Vasodilators.They are used to relax the smooth muscles of blood vessels, expand the lumen between them, relieve pain in small vessels and eliminate night pain.Vasodilators also improve joint circulation and help deliver nutrients needed by cartilage tissue.When used correctly, vasodilators provide a significant therapeutic effect.However, the effectiveness of the treatment is affected by the individual tolerance of the drugs.
- Chondroprotectors(medicines that restore cartilage).They are the most effective modern drugs, as they influence the restoration of cartilage tissue and nourish it with the necessary substances.With regular use of chondroprotectors, it is possible to stop the development of coxarthrosis.The positive result appears over time, and after the end of taking the drug, the cartilage recovery process will continue.
Surgical treatment of coxarthrosis
Surgical intervention is resorted to in case of significant destruction of the cartilage tissue, the impossibility of its restoration and immobility of the joints.In some cases, surgery is the only possible way to restore a person's ability to walk without pain.
Endoprosthesis is an operation to remove the affected joint and replace it with an artificial analogue - an endoprosthesis.The shape of the endoprosthesis resembles a real joint, it performs all the functions of the joint and can withstand high loads when walking, running, etc.
Service life of the endoprosthesis
Like anything, an endoprosthesis has its own service life.Endoprosthesis wear depends on loading and mobility.Excess weight significantly increases the load, and the service life of the prosthesis will be about 10 years.With moderate loading and mobility, the endoprosthesis will last about 15 years.There are also models of prostheses whose service life is 20-25 years, but their main drawback is the high price.
After wear of the endoprosthesis, a repeat operation is required for its replacement.However, replacement of the prosthesis is complicated by the fact that the hip bone thins over time and the problem of fixing the prosthesis arises.Therefore, in order to avoid repeated endoprosthetics, it is necessary to use conservative methods of treatment as long as possible.
It is worth mentioning the risks of hip replacement - the number of deaths after surgery is 1-2%.
Rehabilitation after endoprosthesis
Joint replacement surgery is quite complex and it will take time to restore lost mobility.The recovery period includes methods to strengthen the body: massage, gymnastics and breathing exercises.The volume and complexity of the loads should be increased gradually so that the body gets used to all the changes.
A healthy diet also speeds up the healing process.It is recommended to include foods rich in phosphorus and phospholipids in the diet, as their properties contribute to the restoration of cartilage tissue.
The rehabilitation period lasts about 6 months.The patient is in the hospital under observation for 5 to 10 days.Then a set of rehabilitation measures aimed at strengthening the hip muscles is carried out.First, the patient will have to walk with crutches, then with a cane, and finally on his own, without any support.
At the end of the rehabilitation period, the patient regains his lost ability to work and the joy of light walking!
Prevention of coxarthrosis
To prevent coxarthrosis, it is necessary:
- adhere to an active lifestyle (do morning exercises, take short walks);
- do not engage in sports professionally;
- maintain a balanced diet, as this helps to avoid weight gain, which causes additional stress on the joints;
- take a course of chondroprotectors once every 1-2 years after 40 years (in case of family predisposition to coxarthrosis or joint injuries).

















































